|
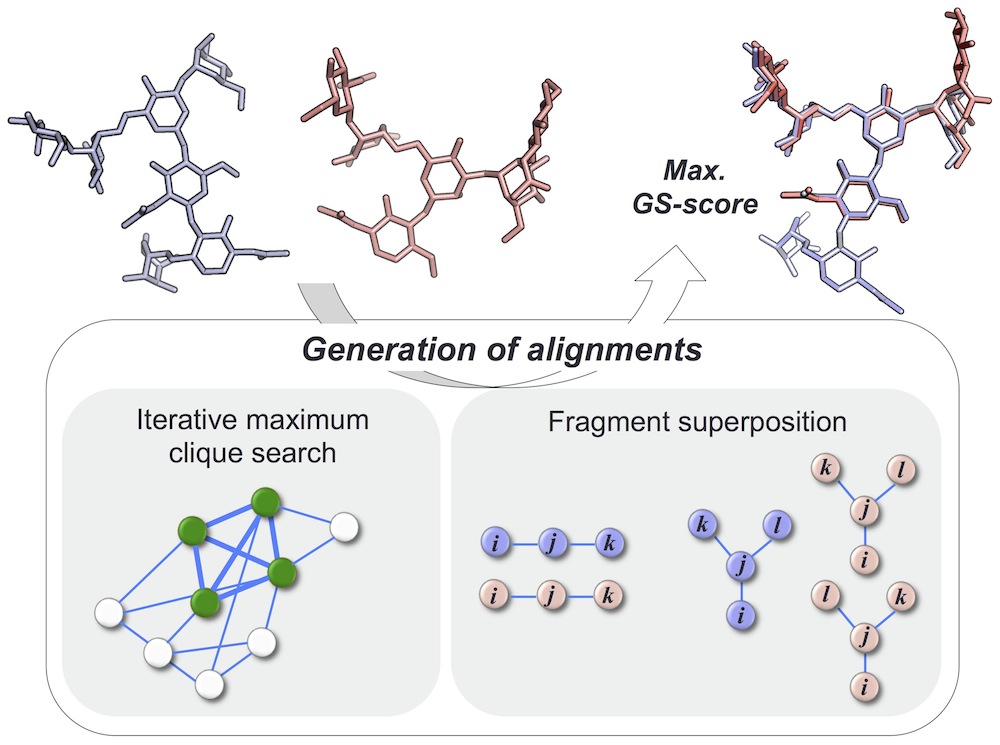
Glycans play critical roles in many biological processes, and their structural diversity is key for specific protein-glycan recognition. GS-align is a novel computational method for glycan structure alignment and similarity measurement. GS-align generates possible alignments between two glycan structures through iterative maximum clique search and fragment superposition, and the optimal alignment is determined by the maximum structural similarity score, GS-score whose significance is size-independent.
|
|
|
1. Installation |
|
Click here to download the GS-align software package including example PDB glycan structures.
The source code of GS-align (gsalign.cpp) is written in C++ and can be easily compiled using C++ GNU compiler by
|
|
|
>g++ -c gsalign.cpp
>g++ -o gsalign gsalign.o
|
|
2. Preparing input glycan structures |
|
Input glycan structure files for GS-align must be in PDB format and be ended with "TER". Users can prepare an input structure by manually extracting the glycan coordinate data from a PDB file. We also recommend use of Glycan Reader (http://www.charmm-gui.org/input/glycan), which is our web-based tool for automated glycan identification and simulation preparation (Jo et al. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32: 3135-3141).
|
|
GS-align needs information on which glycosidic oxygen is linked to which residue for the calculation of GS-score. However, it is not easy to manually assign the glycosidic oxygen information only based on the context in the PDB file. The GS-align software package contains an auxiliary program (AssignOGAtoms.java) to automatically assigned the glycosidic oxygens after renumbering the residue sequences.
|
|
>javac AssignOGAtoms.java (for compile)
>java AssignOGAtoms [glycan structure file in PDB format] (for execution)
|
|
3. Running GS-align |
|
-s1 |
glycan structure 1 (PDB format) |
|
-s2 |
glycan structure 2 (PDB format) |
|
-n |
GS-score normalization option (default = 1)
1: normalize using larger glycan
2: normalize using smaller glycan
3: normalize using -s1 structure
|
|
-o |
output option (default = 1)
1: score only
2: score, superposed -s2 structure with matrix, and sequence alignment
|
|
(Example) >gsalign -s1 1L6X_A_glycan_OG.pdb -s2 4KU1_B_glycan_OG.pdb -n 1 -o 2
|
|
4. Outputs |
|
GS-score |
calculated using all aligned residue pairs |
|
RMSD (Å) |
calculated using aligned residue pairs within 5 Å |
|
ali_struct.pdb |
the PDB coordinates of -s2 structure aligned onto -s1 structure |
|
matrix.txt |
translational and rotational matrix to align -s2 structure onto -s1 structure |
|
Seq. Alignment |
a list of -s2 residues aligned onto -s1 residues within 5 Å |
|

